The Journey Begins: The HMS Beagle
In 1831, a young naturalist named Charles Darwin embarked on a five-year voyage aboard the HMS Beagle. The journey took him to various parts of the world, including the Galápagos Islands, where he observed unique species of plants and animals. These observations sparked Darwin’s curiosity about the diversity of life and the processes that drive evolution.
Image: The HMS Beagle, the ship that carried Darwin on his voyage around the world.
The Theory of Natural Selection
Over the next two decades, Darwin meticulously gathered evidence and developed his theory of natural selection. He proposed that species evolve over time through a process where individuals with traits better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. These advantageous traits are then passed on to future generations.

Image: A diagram illustrating the concept of natural selection, where favorable traits are passed down.
The Publication of “On the Origin of Species”
On November 24, 1859, Darwin published his groundbreaking work, “On the Origin of Species.” The book presented his theory of evolution by natural selection and provided extensive evidence to support it. The publication was a scientific milestone, challenging the prevailing views on the origins of life and sparking widespread debate.

Image: The cover of the first edition of “On the Origin of Species” published in 1859.
The Impact on Science and Society
Darwin’s ideas were revolutionary and controversial. The concept of evolution challenged the traditional views held by many religious and scientific institutions. However, as more evidence accumulated, the scientific community gradually accepted Darwin’s theory, recognizing it as a fundamental principle of biology.

Image: A historical debate among scientists and scholars discussing Darwin’s theory of evolution.
The Legacy of Darwin’s Work
“On the Origin of Species” has had a profound and lasting impact on science and society. Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection has become a cornerstone of modern biology, influencing fields as diverse as genetics, ecology, and paleontology. His work also sparked new discussions about humanity’s place in the natural world.

Image: A statue of Charles Darwin at a museum dedicated to his contributions to science.
Exploring Darwin’s World Today
Today, Darwin’s legacy is celebrated in museums, educational institutions, and natural history sites around the world. Visitors to the Galápagos Islands can see the landscapes and wildlife that inspired his theories, while museums like the Natural History Museum in London offer exhibits on his life and work.
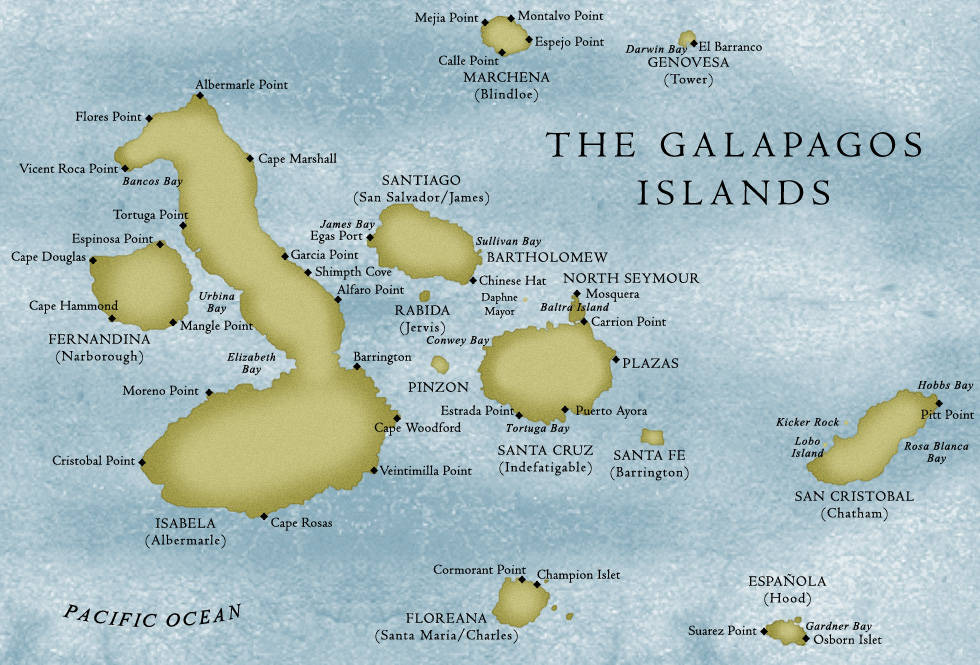
Image: The Galápagos Islands, where Darwin observed the unique species that influenced his theories.
Conclusion: A Landmark in Scientific Thought
The publication of “On the Origin of Species” in 1859 marked a turning point in our understanding of life on Earth. Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection continues to shape scientific thought and inspire new generations of researchers, making it one of the most important works in the history of science.

Image: The Natural History Museum in London, where Darwin’s contributions to science are honored.